“The Importance of Digitalization in Vocational Education and Training (VET)
In an era marked by rapid technological advancements and evolving labour market demands, the digital transformation of Vocational Education and Training (VET) has become a strategic priority at the European level. The European Commission, through a comprehensive policy framework, has underscored the significance of digitalization in modernizing and strengthening VET’s excellence, innovation capacity, and attractiveness. This framework includes initiatives such as the European Education Area, the Digital Education Action Plan (2021-2027), the Council Recommendation on the key enabling factors for successful digital education and training, the Council Recommendation on Vocational Education and Training, and the Osnabrück Declaration. These policy instruments and initiatives collectively emphasize the role of VET in equipping learners with the skills and knowledge needed to thrive in the digital economy, while also highlighting the importance of digital tools in enhancing the accessibility, flexibility, and inclusivity of VET programs.
Central to the digital transformation of VET is the upskilling and reskilling of teachers and trainers in the effective use of digital tools. The European Commission has emphasized the importance of empowering educators to confidently integrate digital technologies into their teaching practices. The Erasmus+ funded project “Di-struct! – Restructuring subjects by digitalizing VET” exemplifies this commitment by providing teachers with the necessary methodology, practical examples, and a curated list of digital tools tailored to different subjects. This project empowers educators to create engaging and effective online courses, thereby contributing to the modernization and digitalization of VET.
Complementing the project’s practical approach are the SELFIE (Self-reflection on Effective Learning by Fostering the Use of Innovative Educational Technologies) self-assessment tools developed by the European Commission. SELFIE for Schools, SELFIE for Teachers, and SELFIE for Work-Based Learning (WBL) offer frameworks for institutions and educators to reflect on their strengths, identify areas for improvement, and chart a course toward effective integration of digital technologies. The insights gained from SELFIE self-assessments can further inform the utilization of the Di-struct! guidelines, enabling educators to tailor their approach based on their institution’s specific needs and digital capabilities.
The European Framework for the Digital Competence of Educators (DigCompEdu) provides a comprehensive framework for developing the digital pedagogical skills of educators. DigCompEdu outlines a set of competences across six areas, offering a roadmap for educators to enhance their digital literacy, communication and collaboration skills, digital content creation practices, assessment and feedback strategies, and their ability to foster digital learning environments. The Di-struct! project aligns with the goals of DigCompEdu by providing practical guidance and concrete examples of how to utilize digital tools in teaching. By utilizing the Di-struct! guidelines in conjunction with the DigCompEdu framework, educators can effectively enhance their digital pedagogical practices and contribute to the digital transformation of VET.
The inclusion of insights into the GAGNE and SAMR models further enriches the guidelines, offering valuable theoretical frameworks to guide teachers in their digital transformation journey. The translation of these guidelines into the partnership’s languages ensures accessibility for European teachers, promoting the widespread adoption of digital tools and practices in VET across the continent.
I am confident that these guidelines will serve as a valuable resource for VET teachers, enabling them to lead the way in this transformative journey to embrace digitalization and contribute to the excellence, innovation capacity, and attractiveness of VET in Europe.”
João Santos
Consultant on education and training, former senior expert at the European Commission
Lisbon 21 January 2025
The “Di-struct! – Restructuring subjects by digitalising VET” project, funded by the Erasmus+ Programme, focuses on equipping VET teachers with digital skills to transform how classes are delivered using ICT. The project arose from recognizing the urgency for development in education digitalization, as highlighted in European educational policy discussions. However, not all member states have taken concrete action to enable schools to provide education supported by digital tools. The COVID-19 pandemic and the subsequent surge in the use of remote learning and digital tools have underscored the need for VET teachers to acquire the necessary skills and knowledge to use technology effectively and responsibly in their teaching.
The Di-struct! project addresses this challenge by providing VET teachers with the skills and tools they need to digitise their lessons and make them more engaging for students. The project intends to bridge the gap between the recognized need for digitalization in VET and the lack of widespread adoption of digital tools and methodologies in classrooms across Europe.
Objectives of the Guidelines
These guidelines aim to:
- Improve the understanding among VET staff of available digital tools and approaches.
- Enhance teachers’ digital skills in terms of content creation.
- Illustrate the benefits of using Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) in VET.
- Provide an overview of the digital tools best suited for various VET disciplines.
- Offer practical examples of how to use digital tools to create innovative teaching content.
- Provide suggestions and advice for the design and implementation of effective digital lessons.
Context
Importance of Digitization in Education
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, education is undergoing a significant transformation. Digitalization offers numerous benefits, including:
- Enhanced Learning Experiences: Digital tools can create more interactive and engaging learning environments, catering to the needs of today’s tech-savvy generation.
- Personalized Learning: Digital platforms enable customized learning experiences that cater to individual student needs and learning styles.
- Access to a Wider Range of Resources: Digitalization provides access to a vast array of online resources, expanding learning opportunities beyond traditional textbooks.
- Development of Essential 21st-Century Skills: Digital tools help students develop critical skills such as digital literacy, problem-solving, and collaboration, which are essential for success in the modern workforce.
Link to the E-Learning
These guidelines are designed to complement the Di-struct! E-Learning course, which provides VET teachers with a comprehensive overview of digital tools and methodologies. The E-Learning course covers topics such as gamification, interactive presentations, online boards, interactive games, content creation, educational resources, Learning Management Systems, and online collaboration tools. To explore E-learning, the first step is filling this form to get the credential to access.
The guidelines will provide practical examples and specific instructions on how to apply the concepts learned in the E-Learning course to different VET disciplines.
Impact on Teaching Methods
Digitalization has a profound impact on teaching methods, encouraging a shift from traditional, teacher-centered approaches to more student-centered and interactive learning experiences. Digital tools enable teachers to:
- Create more dynamic and engaging lessons.
- Facilitate active learning and student participation.
- Provide personalized feedback and support.
- Promote collaboration and peer learning.
By embracing digital tools and adapting their teaching methods, teachers can create more effective and relevant learning experiences for their students.
Prepare Teachers for the Future of Education
The rapid advancements in technology are transforming the educational landscape. Digitalization is no longer a trend but a fundamental aspect of modern education. By acquiring the necessary digital skills and embracing innovative teaching methodologies, teachers can prepare themselves for the future of education and empower their students to thrive in a digital world.
Each section of the guidelines will be dedicated to a specific VET discipline. Each section will include the following elements:
- Introduction to the discipline and its specific digitalization needs.
- Recommended digital tools with descriptions, benefits, suggested target, if an installation on the laptop is required or not, usage examples, and the link to use it.
- Concrete examples of digitization in professional fields. Please note that the examples of digitization in professional fields contain documents or external links which may not be in your mother tongue. These documents are for information purposes, to show you how the teaching content is structured.
- Best practices for digitizing content, including needs analysis, tool selection, content adaptation, and implementation strategies.
- Methodology: Step-by-step instructions on how to structure and digitalize content effectively.
- Description and comparison of the SAMR and Gagné models, including examples and their relevance to digital content creation.
- Conclusion: Summary of key takeaways and recommendations for further exploration.
- Tips and comments from teachers, sharing real-life experiences and practical advice.
The Di-struct! project and these guidelines are committed to supporting VET teachers on their journey towards digitalization, empowering them to create engaging and innovative learning experiences for their students and contribute to the advancement of VET in Europe.
Benefits for teachers and students
- Increased accessibility of educational material that can be consulted synchronously or asynchronously by students, particularly in different learning situations (FEST = training outside the walls of the CFA, students with phobia or dropping out of school, students with special needs). This accessibility also makes it possible to make the courses accessible in the event of student absences.
- Inclusion of special needs: new technologies also make the transposition of our courses more simple for students with disabilities (voice reading, subtitles, possibility of switching content to dys mode).
- Pedagogical differentiation: digital educational content then makes it possible to adapt to the level of apprentices and avoid boredom for those with a high level and on the contrary discouragement for those with a lower level. AIs adapted to existing tools thus make it possible to quickly target the level reached in an exercise such as Quizlet and adapt to the participant. Some tools also offer feedback that can be easily used by the teacher, who will be able to adapt the next lesson according to the results obtained.
- Engaging and interactive content: the idea is not to multiply the tools in a senseless and thoughtless way, but some of them, extremely simple in their use, can bring dynamism and a necessary bounce back in the classroom. Especially in the case of a virtual classroom where the students’ attention is all the more of an issue.
- Efficiency and time saving: finally, familiarization with these tools allows you to gain in efficiency and therefore to save time in your pedagogical practice (to be reused elsewhere on a more personalized support for apprentices or other). Once you get the hang of it, the digital tool can therefore facilitate the teacher’s work by allowing them to reuse canvases that have already been established or by updating them.
Other benefits can be mentioned¹:
¹ How Technology is Changing Education? The Journey from Whiteboard to Keyboard https://www.apogaeis.com/blog/how-technology-is-changing-education-the-journey-from-whiteboard-to-keyboard/
Impact on teaching methods
Prepare teachers for the future of education (adaptation to digital environments, collaborative tools, etc.) and the evolution of society in general.
It is also a question of meeting the requirements of the labour market in which our apprentices are engaged. Mastery of software, use of collaborative tools, online tools – including in remote fields at the base of digital technology. Putting them in contact with digital technology as soon as possible also promotes their adaptability to future technological developments related to their professional field.
The school thus connects more to the professional world. Digital technology allows apprentices to get into the swing of their future professional practice and to project themselves.
The skills mobilized are also transversal and transferable to other fields. Learn to work remotely, learn to manage a schedule, encourage autonomy and critical thinking.
Opening up pedagogy to digital technology finally allows us to question the best practices to adopt, to promote an ethics of this use among our apprentices. This generally contributes to the formation of responsible citizens, aware of the ethical issues of digital technology.
Autonomy of future citizens after the school system. Teaching also means thinking about the + distant future of our apprentices and encouraging them to always improve their skills. Digital technology also plays a role in this evolution.
– New Gen-Z and Alpha methodology?
Gen Z (1997-2012) Gen Alpha (post 2013), globally the “digital natives”. Generations more used to short, dynamic and interactive content. They use social media on a daily basis, so the pedagogy going digital “speaks” to them more. Digital technology therefore represents an interesting learning lever to be mobilized for the commitment, interest and motivation of these apprentices who appreciate autonomy and interactivity.

To go further:
- EU support for the digitalisation of schools; 2023 (English version only)
- Digital Education Action Plan (2021-2027); (English version)
- How Technology is Changing Education? The Journey from Whiteboard to Keyboard
1. Note taking “Study smarter not harder”
- VET subject: Computer Science in a technical economic school, teaching coding to accounting students
- Overview: This learning unit focuses on enhancing students’ study autonomy through effective note-taking methods, time management strategies and the integration of digital tools. The addresses the challenges they face, such as difficulty organizing study time, low digital literacy, and inclusion of students with special needs.
The subject is highly transversal, as it supports all disciplines by equipping students with essential skills that improve comprehension, retention, and school performance. - Link to the learning unit: Note taking “Study smarter not harder”
2. Exploring fruit and vegetables in culinary technology
- VET subject: Culinary Technology
- Overview: This learning unit focuses on enhancing students’ understanding of Culinary Technology. Students will learn to identify and classify fruits and vegetables, understand quality and storage criteria, and comply with regulations. The unit combines theory and practice, emphasizing sustainable food practices and consumer demands. Interactive tools and gamification are used to motivate students, with assessments conducted through Microsoft FORMS and Escape Games on GENIALLY.
- Link to the learning unit: Exploring fruit and vegetables in culinary technology
3. Practice in 3D engineering design software systems
- VET subject: Practice in 3D engineering design software systems
- Overview: 3D Modeling, is a method used to create computer models of real-world objects for applications in machine engineering. At the heart of “Practice in 3D engineering design software systems” course is applied geometry where complex geometrical models are created by manipulating and combining basic shapes such as cubes, rectangular prisms, cylinders, spheres, and cones. In this course students learn CAD/CAM engineering software through hands-on practice. While building 2D and 3D models, they improve their geometry skills and develop strong spatial reasoning skills (ability to “think in the 3D space”). Upon completing the course, students are ready for a smooth transition to using professional CAD software such as Solide Egde engineering design software.
- Link to the learning unit: Practice in 3D engineering design software systems
4. Business and databases
- VET subject: Business and databases
- Overview: The main goal of this unit is to provide students from both courses with management and database structuring skills/expertise. Students from the Business Course should explain the requirements for creating a customer database that meets the needs of the commercial department and students from the IT Systems Management and Programming course should exchange concepts about database structure requirements. The joint activities help students to see how different areas of management are interconnected in the context of a real company. Activities include research, Teamwork using Canva to create presentations, Whiteboard to create interaction between the two classes with assessments conducted through Moodle Quiz and Kahoot.
- Link to the learning unit: Business and databases
5. Food4all
- VET subject: Cooking Technology, Restaurant Management and Bar-Tendering
- Overview: This unit focuses on enhancing students’ understanding of Italian regional foods and drinks, with an emphasis on their labeled products. It aims to build culinary vocabulary in English and Italian and develop skills in planning and presenting projects. Activities include research, digital content creation, and a Kahoot battle to assess knowledge. Students work on individual and team tasks using tools like Canva, Padlet, and Google Slides to create engaging presentations. The approach encourages collaboration, digital proficiency, and self-assessment, fostering confidence and creativity.
- Link to the learning unit: Food4All
6. Fascism and Futurism Decades
- VET subject: Food Service and Bar Tendering, Food Science
- Overview: It explores the rise of Fascism in Italy and its social, political, and cultural impacts, particularly focusing on propaganda’s role in shaping Italian gastronomy and beverage culture. Students analyze the influence of intellectuals, such as Futurists, on Fascist ideals and study how food and drinks became tools for national identity. Activities include case studies, creative tasks like designing propaganda-inspired cocktails, and debates to enhance understanding. The unit employs digital tools like Youtube videos to provide inspiration and PowerPoint or Canva to foster collaboration and critical thinking.
- Link to the learning unit: Fascism and Futurism Decades
7. Foundations of machine engineering
- VET subject: Machine Manufacture design
- Overview: A complex two-grade subject including engineering drawing, mechanical materials, safety at work, and basic metalworking. It helps to develop the students’ mechanical engineering mindset. Learners will be able to carry out tasks with responsibility and make decisions in project work. The course is an important part of the sectoral basic examination.
- Link to the learning unit: Foundations of machine engineering
8. Circular Economy, Start-Ups and Anti-waste Catering
- VET subject: Food and Wine Service, Food Science, Economics
- Overview: This unit addresses sustainability through topics like Agenda 2030, Circular Economy, Green Economy, and Food Waste, emphasizing the future of sustainable catering. It combines gamification, cooperative learning, and digital tools to explore critical consumption, startups, and green practices in various industries. Activities include quizzes, videos, case studies, and creative tasks like recycled crafts and escape room creation. Tools like Canva, Mentimeter, and Google Docs foster collaboration and engagement while enhancing language skills via CLIL methodology. The focus is on empowering students to connect global challenges with practical solutions.
- Link to the learning unit: Circular Economy, Start-Ups and Anti-waste Catering
9. Converting Masses in Culinary Arts
- VET subject: Culinary Technology
- Overview: This unit focuses on improving apprentices’ ability to convert measurements in the kitchen, addressing the challenge of applying theoretical math skills to practical tasks. It enhances their speed, autonomy, and accuracy in using kitchen tools and following recipes.
The subject is transversal, supporting various culinary disciplines by equipping apprentices with essential skills to work efficiently and accurately, with the help of digital tools like WOOCLAP, SWAY, and QUIZLET. - Link to the learning unit: Converting Masses in Culinary Arts
Prerequisites
Am I comfortable with digital tools?
☑ Yes: list and bookmark the available tools. When there are many of them, remember to classify them according to their uses (quizzes, presentations, exercises, memorization, getting people to collaborate, practising speaking, working on writing, etc.).
☐ No: apply the First Small Step Possible method, i.e., choose a small educational action (welcome, end of class, an exercise, etc.) to dare to get started. Target a tool that is available and if possible mastered by a colleague to get help easily. Another solution is to watch a tutorial to get to grips with the tool more quickly.
Methodology: Basic steps to structure and digitize content (needs analysis, selection of tools, design of digital resources).
1. Needs analysis
- What are the skills to be developed provided for in the framework (according to Bloom’s taxonomy: knowledge, understanding, application, analysis, synthesis, creativity/evaluation)?
- What are the specific learning objectives (content, behavior, conditions)? E.g. “At the end of the activity/lesson, the student will be able to use the targeted vocabulary in the various contexts of his or her profession.”
- What kind of knowledge do learners acquire? Declarative knowledge (vocabulary, comprehension, concept) or procedural knowledge (automatisms, know-how, method)?
- When would a digital tool be relevant? For example: beginning of the session (reactivation, prerequisites, surprise effect or complex question, …), during the session (to summarize, check understanding, practicing, …), at the end of the session (summarize, question, announce the rest, …), during an evaluation or a complex task, for work to be done at home. Or for example :
- Why would a digital tool be relevant?
To take into account the 4 pillars of learning:
☑ Attention: capturing and keeping attention can be facilitated by digital tools. Ex : use Classroom-screen to create a stimulating virtual environment.
☑ Active engagement: Every learner should be able to participate. Ex : incorporate Wooclap for interactive real-time polls and quizzes.
☑ Feedback: Instant feedback is very effective. E.g . use Quizlet for self-correcting exercises or Wooclap for collective remediation.
☑ Consolidation: forgetting happens very quickly! Short, regular and spaced practice helps to counter forgetfulness and memorize! E.g . offer Learning-Apps or Quizlet for review activities.
To make training courses accessible to all (e.g . disability, neuro-atypical, absent) and/or to offer a variety of assessment materials or learners’ choice (universal design of learning).
To promote multimodality in the presentation of knowledge, proposed learning tasks and assessments. E.g . face-to-face/remote, synchronous/asynchronous, auditory, visual (static/dynamic), …
To make experiences possible that are impossible without digital technology. E.g . collaborating on the same document at the same time; collaborating remotely; carrying out scientific experiments without risk, without equipment, without consumables; talking to a virtual teacher who asks questions; being corrected in real time, etc.
→ teacher’s choice of a tool, activity, theme and learning objective
→ choice by the learner of a deliverable medium (audio, video, written, mind map, quiz, …)
Content creation
- What media do I already have? E.g . books, digital books, course materials, exercise sheets, teachers’ websites, etc.
- Can I adapt/integrate these media?
☑ Yes: use screenshots, existing files to import them into digital tools directly or via the tool’s AI.
☐ No: check whether similar content is available online, in the databases.
☑ Yes: use them as is or adapt them
☐ No: Create your own content
- How can I personalize the content? With elements of the profession, the course, the institution, the group (e.g. choice of examples, photos, videos, …)!
- How to classify the various digital resources? You can classify the digital resources in the tools themselves, in folders, in your browser’s favorites, etc.
Implementation
- Create a session or a sequence integrating one or more tools directly into your workspace (Moodle, Yparéo, Pronote, etc.) or on other media.
- Integrate the different media and digital tools in a coherent way in the course. E.g . copy/paste internet links or QR codes to integrate these digital activities, find them easily or offer them to learners synchronously or asynchronously.
- Plan to deal with technical issues (e.g . wifi, internet connection) and time to appropriate the tools with the learners.
Evaluation and continuous improvement
- How did the learners perceive the proposal? Have they understood the pedagogical intentions and the interest of the proposed task (metacognition)? How can the practice be improved? To question them to gather their opinions and make them actors in their training. (e.g . orally, in writing, using digital tools such as Forms).
- What were the obstacles to learning and how can they be overcome? E.g . technique, cognitive overload, instructions, time, too “easy” or too “hard”, lack of explanations…
- How to track learners’ progress? Formative assessments are powerful training tools because they allow learners and teachers to measure progress and address challenges. Digital assessments allow all learners to assess themselves, train their long-term memory, counter forgetfulness and identify difficulties. They allow the teacher to monitor progress and to take over the points not acquired. E.g . Wooclap, Quiziniere, Learning-Apps, Quizlet, Quizziz, GoogleForm, are all tools for this.
- Do I need training to progress in the use of digital technology?
☐ No: the practice and use of digital tools naturally allows me to progress and gain in speed and automatisms
☑ Yes: I reach my limits. I’m looking for training or other tools! E.g . with colleagues, watching tutorials or participating in webinars, browsing galleries of examples, requesting Adhoc training, following MOOCs, subscribing to educational newsletters, following inspiring sites or accounts, etc.
Short description: Microsoft Whiteboard provides an intelligent, free-form canvas for imagining, creating and collaborating visually. It lets you write or draw, enter text, add an image, sticky notes or a note grid to express your ideas, and use feedback to visually communicate your thoughts.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students
Example of application: Business and databases
Installation required: yes (app)
Link: www.microsoft.com/en/microsoft-365/microsoft-whiteboard/digital-whiteboard-app
Short description: Kahoot! is a playful learning platform. It includes learning games such as multiple-choice quizzes. It is accessible via a web browser, but can also be downloaded to a smartphone. This educational platform is similar to other technological learning tools such as Wooclap, Wooflash, Socrative and Quizlet.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students
Example of application: Business and databases , Practice in 3D engineering design software systems
Installation required: no
Link: https://kahoot.com/
Short description: A web-based presentation tool allowing users to create, edit, and share presentations.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students, individual students, teachers
Example of application: Foundations of machine engineering
Installation required: no
Link: https://workspace.google.com/intl/en_uk/products/slides/
Short description: Miro is a digital collaboration platform designed to facilitate remote and distributed team communication and project management.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students, individual students, teachers
Example of application: Note taking “Study smarter not harder”
Installation required: no
Link: www.miro.com
Short description: Evernote is a versatile note-taking tool designed to help you organize your ideas, tasks, and projects. It allows you to create notes, save web content, manage to-do lists and collaborate seamlessly across devices, ensuring information is always available.
Suggested target: individual students
Example of application: Note taking “Study smarter not harder”
Installation required: no
Link: http://www.evernote.com
Short description: Microsoft OneNote is a digital notebook that allows users to capture, organize, and share notes across devices. With features like text, drawings, images, and multimedia support, it’s perfect for managing tasks, collaborating on projects, and keeping ideas in one place.
Suggested target: groups of students, individual students, teachers
Example of application: Note taking “Study smarter not harder”
Installation required: no
Link: https://www.onenote.com/
Short description: A graphic design platform that offers various templates and tools for creating infographics, posters, presentations, and more.
Suggested target: groups of students, individual students, teachers
Example of application: Food4All
Installation required: no
Link: http://www.canva.com
Short description: Microsoft PowerPoint is a presentation software. It is part of the Microsoft Office suite. It can be used to create both simple slide presentations and complex slide shows.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students, individual students, teachers
Example of application: Fascism and Futurism Decades
Installation required: no, available offline as well
Short description:
Lib Manuels is a digital platform offering a digital and interactive version of textbooks and educational resources for students and teachers. It provides easy access to a wide range of digital learning materials, enhancing teaching and learning experiences through interactive tools and seamless navigation.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students, individual students
Example of application: Exploring fruit and vegetables in culinary technology
Installation required: no
Short description: A digital tool that allows us to create interactive exercises, presentations, images, quizzes, portfolios and much more. In this tool you can enrich your classes with animation and interactivity within seconds.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students, individual students
Example of application: Exploring fruit and vegetables in culinary technology
Installation required: no
Link: https://genially.com/
Short description: Google Forms is a survey administration software included as part of the web-based Google Docs Editors suite. Google Forms is only available as a web application. It allows users to create and edit surveys online and to collect information into a spreadsheet.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students, individual students, teachers
Example of application: Exploring fruit and vegetables in culinary technology
Installation required: no
Short description: OER Commons provides a curated collection of free and open educational resources for teaching and learning. This platform offers a variety of high-quality materials, including lesson plans, activities, and interactive content, empowering educators to share, discover, and customize resources for their classrooms.
Suggested target: teachers
Example of application: Practice in 3D engineering design software systems , Foundations of machine engineering
Installation required: no
Link: https://oercommons.org/
Short description: Edpuzzle is an interactive learning platform that allows teachers to create engaging video lessons. Educators can customize videos by adding questions, notes, and voiceovers to track student progress and understanding, making learning more personalized and effective.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students
Example of application: Practice in 3D engineering design software systems
Installation required: no
Link: https://edpuzzle.com/
Short description: Video platform to show videos to your classroom.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students, individual students
Example of application: Practice in 3D engineering design software systems
Installation required: no
Link: https://www.youtube.com/
Short description: Baamboozle provides an easy and enjoyable way to teach through games that are both engaging and tailored for students. With a wide variety of games and a user-friendly editing tool, the platform allows the community to create and customize content.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students
Example of application: Foundations of machine engineering
Installation required: no
Short description: A learning management system that enables teachers to create, distribute, and manage assignments, resources, and assessments.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students
Example of application: Circular Economy, Start-Ups and Anti-waste Catering
Installation required: no
Link: https://edu.google.com/intl/ALL_uk/workspace-for-education/classroom/
Short description: Mentimeter is an online platform for creating polls, surveys, interactive questionnaires and real-time presentations. It is used to interact with the public and gather responses. Here are some of the main features offered by the tool: Dynamic word clouds; Live interactive polls; Quizzes; Surveys
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students
Example of application: Circular Economy, Start-Ups and Anti-waste Catering
Installation required: no
Short description: Quizlet allows teachers to create digital flashcards and quizzes. It can also be used to create multiple-choice, true/false and fill-in-the-blank tests.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students
Example of application: Converting Masses in Culinary Arts
Installation required: no
Link: https://quizlet.com
Short description: A survey and quiz creation tool that enables teachers to create assessments and gather feedback.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students
Example of application: Converting Masses in Culinary Arts
Installation required: no
Link: https://www.wooclap.com/
Short description: Sway is a Microsoft Office application that allows you to easily create and share interactive reports, personal stories, and presentations without needing design skills.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students
Example of application: Converting Masses in Culinary Arts
Installation required: no
IF YOU WOULD LIKE TO DISCOVER MORE DIGITAL TOOLS, YOU CAN HAVE A LOOK AT THESE SLIDES
The chapter of ” Why digitalize educational content?” focused on the students’ benefits of digitally enhanced lessons, in other words you can understand the WHY. In this chapter, we introduce you to the HOW and present two models for digitizing lessons that you can use easily and effectively in your everyday teaching practice. Both are closely linked to the findings and outcomes of the project. These two models are SAMR and Gagné’s Nine Events of Instruction. But whichever one you use, your pedagogical goal always must be to find the right tools for your learners. To develop the right learner focused technology integration, you have to think about a few key questions:
- How can Your lesson be improved using technology?
- How can You engage and empower students through technology?
- How can digitally enhanced learning closely resemble authentic, real-world learning?
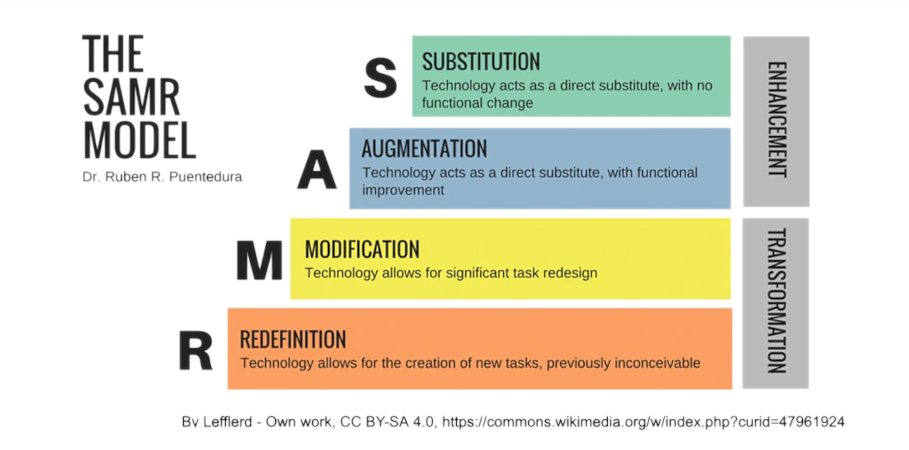
SAMR – the model for understanding the right integration of technology and EdTech
The model, which has been in use since the mid-1990s, is based on the fact that there are different stages of integration of digital tools and technologies in education. It is a hierarchical model, which assumes that there is a clear qualitative difference between each level and that moving from one level to another needs teaching/learning pedagogical innovation for the institution, teacher, and student group (class).
Furthermore, the model states that the educational integration of technology at each level depends on the level of teachers’ and learners’ digital pedagogical and learning competences and knowledge of using EdTech tools, the scale of their application (what they are used for: digital content, online learning, knowledge assessment, communication between the stakeholders, active cooperative learning, etc.) and, last but not least, the development level of the institutional (school) policy, practices and culture (innovative open educational supportive climate) that support the EdTech integration into the teaching and learning process.
Let’s see the four hierarchical levels of technology integration:
S – Substitution. Technology just replaces a traditional teaching activity and/or material in the educational practice without a significant methodological change. This could be the use of digital presentation tools instead of writing on a blackboard, the use of pdf, e-book instead of the traditional textbook, or even an online test and posting online using Microsoft OneDrive, Google Drive, or a similar file-sharing service. If you have only been teaching with classical tools, this could be a good start to integrate EdTech tools into your teaching practice.
A – Augmentation. In comparison to simple substitution, the use of technology in education at this level means extending the learning process with digital tools that support learner interactivity and involvement. The use of technology gives an opportunity for interactivity, learner feedback, and active involvement of the learner in the learning process, but the use of traditional methodology is typical. An example could be, when students receive immediate feedback on their performance from the teacher or peers, for example using Kahoot, LearningApp, or Quizizz. However using a Padlet also allows for active learner engagement.
In the first two levels, the integration of EdTech can improve student engagement by making learning more fun and playful, but in the longer term, if we don’t change the tools we use, this motivation improvement may disappear.
M – Modification. At this level, EdTech tools allow us to change the teaching and learning process, to change the roles of the teachers and learners, thus improving skills to make the learning flexible and meet the learning needs of the students. It allows the development of 21st century competencies too. These could be the implementation of online or blended/hybrid project activities, where learners can work independently, in groups online, research, find information, and think together to create a subject-specific product while developing important skills.
R – Redefinition. At this level a complete rethinking of teachers’ work and activities, change in the content and learning processes, with the integration of technology for learning are taking place. This enables learners to learn through solving creative problems that were not possible before. Using VR and AR, virtual work placements (even international ones) can be implemented. Technology also provides opportunities to bring authentic audiences into the virtual classroom. Students can tackle local problems and invite members of the community to assess their digital proposals.
Gagné’s model for increasing learning engagement of the students
The following model is an excellent way of enriching a teaching module, a lesson, or a learning unit, by using an EdTech tool and thus improving the learning motivation and experience of the learners. The basis of this extremely usable model in practice is to identify the points of the learning process where the learner’s learning motivation can be influenced using traditional and/or digital tools. Although originally Gagné did not develop the model for enriching learning/teaching with the use of digital tools, the model is perfectly suited for this purpose. What is important for 21st century education is what EdTech tools can be found to influence learner effectiveness at these points of stimulation identified by Gagné. The tools need to fit the learning behaviours and needs of learners in the 21st century, so they need to be EdTech tools as well.
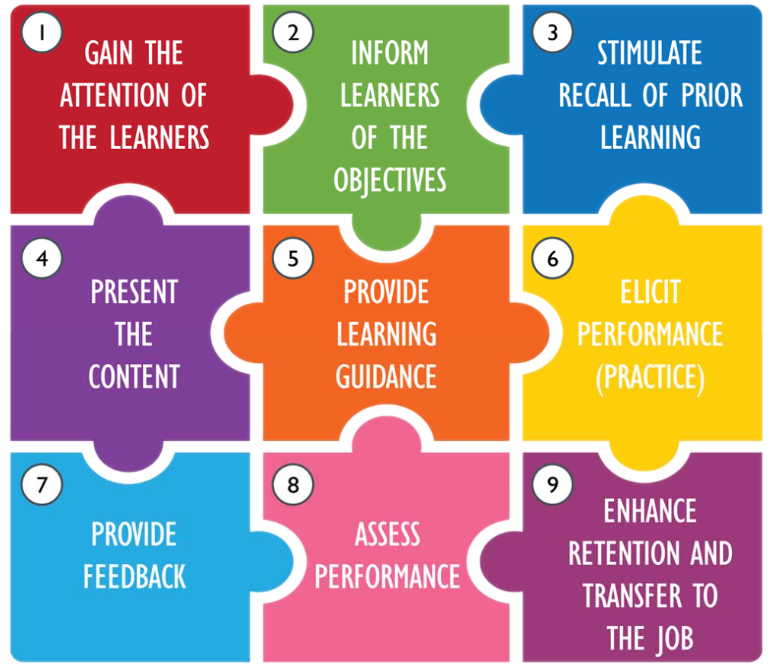
Using the model, you, as a teacher must identify to stimulate the learners’ motivation on the following points during the learning process:
- Gain attention – Get the students primed and focused, so they are ready to learn the topic at hand. Use animations, videos, interactive stuff & games, VR/AR tools, and give them tasks
- Inform learners of objectives. –Tell students what they will learn during the lesson to get them in the proper state of mind so they can anticipate what they will need to do afterward. Use visual communication tools, like Canva; LMS Tools, like Moodle, Google Classroom, Blackboard; Goal-Setting Apps, like Trello,
- Stimulate recall of prior learning – Prime students for learning new material by refreshing their memories of prior-learned content. Use Kahoot, Quizlet, Quizzes, Baamboozle, flashcards, or any other quiz tool (stand-alone or integrated with any LMS system)
- Present the content – Once the environment is ready and students are receptive and primed, it is time to teach the applicable lesson. Use video platforms, Edpuzzle (interactive video), TED-Ed; Interactive presentations, like Genially, SlideShare, Haiku Deck, Interactive/digital eBooks, and customizable LMS, like Moodle
- Provide “learning guidance” – Explain clearly to students what is expected for them to understand and any instructions needed to achieve successful outcomes. Use guided practice tools, like Khan Academy, PhET Interactive Simulations; Real-Time Feedback: Classkick, Formative; Digital Note-Taking: Evernote, Notion, OneNote, and AI Tutors
- Elicit performance (practice) – Instruct students to practice or demonstrate their newfound knowledge so it can be assessed. Use Interactive exercises, simulations, digital labs, and games to practice. H5P (interactive content creation), Kahoot, Mentimeter, online project collaboration tools, like Google Workspace (Docs, Sheets, Slides), Microsoft Teams, and/or customised LMS, like Moodle.
- Provide feedback – Offer immediate feedback on student tasks that is personalized, constructive, and positive. Use online/blended/hybrid tools for peer/group/teacher feedback;
- Assess performance- Conduct a comprehensive assessment to determine how well students met their learning objectives so learning gaps can be addressed. Use Kahoot, Quizlet, Quizzes, Baamboozle, flashcards, or any other quiz tool (stand-alone or integrated with any LMS system). Adaptive Testing Tools, H5P, and Game-Based Assessments, like Minecraft Education Edition, ClassDojo, Digital Portfolios: Seesaw, and Google Sites.
- Enhance retention and transfer – Teachers should do everything possible to help students retain the information they worked so hard to learn and give them chances to personalize their learned experience to apply it to their own life or job. Use Scenario-Based VR Tools, simulations (OpenSimulator), E-Portfolios, Real-Life Applications like Google Earth (geography projects), Wolfram Alpha (real-world math/science).
Further readings
The Di-Struct project has demonstrated that digitalization in Vocational Education and Training (VET) is not just an option but a necessity for modern teaching. By integrating digital tools, interactive methodologies, and adaptive learning strategies, educators can significantly enhance student engagement, accessibility, and skill acquisition.
Moreover, digital tools play a crucial role in lifelong learning, enabling both teachers and students to continuously update their knowledge and competencies in an ever-evolving technological and professional landscape.
In this context, digital resources not only facilitate the learning process but also help educators stay aligned with industry advancements, ensuring that vocational training remains relevant and effective.
However, this transformation requires a structured approach, ongoing experimentation, and strong institutional support to maximize the benefits of digital education.
Key Insights from the teachers after the Testing Phase
- Digitalization increases engagement, but balance is key
- Tools like LearningApps, Kahoot, Wooclap, and Microsoft Whiteboard enhanced student participation, making lessons more interactive.
- However, excessive or unstructured use of digital tools can overwhelm students and teachers, making it crucial to carefully align technology with learning objectives.
- Personalization and accessibility improve learning outcomes
- Digital resources help accommodate different learning paces, special needs, and remote learning situations.
- AI-based tools such as Quizlet and adaptive learning platforms can tailor lessons to individual proficiency levels.
- Blended learning and interdisciplinary approaches work best
- The most successful lesson plans combined digital activities with traditional, hands-on experiences—particularly effective in fields like Culinary Technology, 3D Engineering, and Business and Databases.
- Interdisciplinary collaboration, such as integrating business management with IT applications, helped students make real-world connections between different fields.
- Flipped classrooms require gradual implementation
- Providing students with digital resources before class (e.g., OER videos) was beneficial, but many saw it as extra homework.
- Schools should cultivate a flipped learning culture by guiding students on how to engage with pre-class content.
- Teacher training and collaboration are essential
- Many teachers faced digital literacy challenges and resistance to new tools. However, peer learning and structured training programs improved confidence and innovation in lesson planning.
- Collaborative tools like Miro, Microsoft Teams, and Padlet facilitated teamwork among educators, leading to co-creation of high-quality digital content.
- Challenges remain in infrastructure and digital dependency
- Over-reliance on cloud-based tools poses risks, such as data loss due to platform changes.
- Unequal internet access and device availability created digital divides, requiring backup strategies for offline learning.
Frameworks for Digital Integration
Integrating digital tools into vocational education requires not only technical proficiency but also a well-structured pedagogical approach. The implementation of digital resources must be guided by clear educational objectives, ensuring that technology enhances, rather than replaces, effective teaching strategies.
The adoption of pedagogical models, such as the SAMR Model and Gagné’s Nine Events of Instruction, provides a structured framework that helps educators integrate technology at different levels, from basic substitution to complete redefinition of learning experiences. These models encourage a strategic and thoughtful use of digital tools, ensuring that learning remains engaging, interactive, and aligned with students’ needs. By following such structured methodologies, teachers can create digital lessons that foster student autonomy, critical thinking, and practical application of knowledge, ultimately improving learning outcomes in VET education.
Looking Ahead: A Sustainable Digital Strategy
For VET institutions to fully leverage digital transformation, future efforts should focus on:
Continuous Professional Development: Regular training for teachers on emerging EdTech tools and digital pedagogy.
Structured Digital Learning Strategies: Establishing clear digital policies to balance online and offline learning.
Scalability & Infrastructure Investments: Ensuring internet accessibility, device availability, and long-term digital sustainability.
AI & Emerging Technologies: Exploring Artificial Intelligence for adaptive learning, Virtual Reality (VR) for immersive training, and gamification for motivation.
While digital tools offer numerous advantages, their integration requires teachers to overcome challenges such as adapting to new technologies, managing digital distractions, and rethinking traditional pedagogical strategies. Future training programs should focus not only on digital skills but also on change management and pedagogical adaptation.
The integration of generative AI tools enables teachers to harness this technology to design innovative teaching activities that leverage digital resources while adhering to established pedagogical methodologies. Generative AI proves valuable in both the brainstorming phase—helping educators explore creative approaches and refine learning objectives—and the production of high-quality teaching materials.
As we integrate AI and digital tools into education, it is crucial to ensure ethical use, data privacy protection, and a balance between digital and human interaction to maintain student well-being.
By streamlining content creation and ensuring alignment with effective teaching strategies, AI empowers educators to develop engaging, structured, and pedagogically sound learning experiences that enhance student participation and comprehension.
Final Thoughts
Digital transformation in VET is an evolving process that requires experimentation, adaptability, and collaboration. The Di-Struct project has laid a strong foundation for integrating technology in vocational education, but the key to long-term success lies in continuous learning, iterative refinement, and institutional commitment.
The recommendations and guidelines produced by the Di-Struct project must be continuously adapted and expanded to keep pace with the rapid evolution of digital technologies in education. As new tools, methodologies, and AI-powered innovations emerge, it is essential for educators and institutions to remain flexible, reassess their strategies, and ensure that digital transformation aligns with both pedagogical best practices and the evolving needs of students and industries.
By embracing digital tools strategically and responsibly, educators can empower students with 21st-century skills, preparing them for a workforce that increasingly demands digital proficiency, adaptability, and interdisciplinary problem-solving abilities.
If you would like to explore the E-learning “VET going digital” it is possible by filling this short form: https://www.di-struct.eu/elearning/
An email with the instructions and the credentials will be sent to access e-learning a few days later.
If you would like to use the template of the learning material shared to VET teachers to get your lessons more digital, you can:
- Download this learning unit template and develop your new lesson plan
- Use this Miro board: after testing your new lesson plan with your students, create a similar board to think about what worked, what didn’t, how effective they were, how students responded and what could be improved.
Please explore the Miro board and the VET schools involved as an example.
Do you have any questions?
“The Importance of Digitalization in Vocational Education and Training (VET)
In an era marked by rapid technological advancements and evolving labour market demands, the digital transformation of Vocational Education and Training (VET) has become a strategic priority at the European level. The European Commission, through a comprehensive policy framework, has underscored the significance of digitalization in modernizing and strengthening VET’s excellence, innovation capacity, and attractiveness. This framework includes initiatives such as the European Education Area, the Digital Education Action Plan (2021-2027), the Council Recommendation on the key enabling factors for successful digital education and training, the Council Recommendation on Vocational Education and Training, and the Osnabrück Declaration. These policy instruments and initiatives collectively emphasize the role of VET in equipping learners with the skills and knowledge needed to thrive in the digital economy, while also highlighting the importance of digital tools in enhancing the accessibility, flexibility, and inclusivity of VET programs.
Central to the digital transformation of VET is the upskilling and reskilling of teachers and trainers in the effective use of digital tools. The European Commission has emphasized the importance of empowering educators to confidently integrate digital technologies into their teaching practices. The Erasmus+ funded project “Di-struct! – Restructuring subjects by digitalizing VET” exemplifies this commitment by providing teachers with the necessary methodology, practical examples, and a curated list of digital tools tailored to different subjects. This project empowers educators to create engaging and effective online courses, thereby contributing to the modernization and digitalization of VET.
Complementing the project’s practical approach are the SELFIE (Self-reflection on Effective Learning by Fostering the Use of Innovative Educational Technologies) self-assessment tools developed by the European Commission. SELFIE for Schools, SELFIE for Teachers, and SELFIE for Work-Based Learning (WBL) offer frameworks for institutions and educators to reflect on their strengths, identify areas for improvement, and chart a course toward effective integration of digital technologies. The insights gained from SELFIE self-assessments can further inform the utilization of the Di-struct! guidelines, enabling educators to tailor their approach based on their institution’s specific needs and digital capabilities.
The European Framework for the Digital Competence of Educators (DigCompEdu) provides a comprehensive framework for developing the digital pedagogical skills of educators. DigCompEdu outlines a set of competences across six areas, offering a roadmap for educators to enhance their digital literacy, communication and collaboration skills, digital content creation practices, assessment and feedback strategies, and their ability to foster digital learning environments. The Di-struct! project aligns with the goals of DigCompEdu by providing practical guidance and concrete examples of how to utilize digital tools in teaching. By utilizing the Di-struct! guidelines in conjunction with the DigCompEdu framework, educators can effectively enhance their digital pedagogical practices and contribute to the digital transformation of VET.
The inclusion of insights into the GAGNE and SAMR models further enriches the guidelines, offering valuable theoretical frameworks to guide teachers in their digital transformation journey. The translation of these guidelines into the partnership’s languages ensures accessibility for European teachers, promoting the widespread adoption of digital tools and practices in VET across the continent.
I am confident that these guidelines will serve as a valuable resource for VET teachers, enabling them to lead the way in this transformative journey to embrace digitalization and contribute to the excellence, innovation capacity, and attractiveness of VET in Europe.”
João Santos
Consultant on education and training, former senior expert at the European Commission
Lisbon 21 January 2025
The “Di-struct! – Restructuring subjects by digitalising VET” project, funded by the Erasmus+ Programme, focuses on equipping VET teachers with digital skills to transform how classes are delivered using ICT. The project arose from recognizing the urgency for development in education digitalization, as highlighted in European educational policy discussions. However, not all member states have taken concrete action to enable schools to provide education supported by digital tools. The COVID-19 pandemic and the subsequent surge in the use of remote learning and digital tools have underscored the need for VET teachers to acquire the necessary skills and knowledge to use technology effectively and responsibly in their teaching.
The Di-struct! project addresses this challenge by providing VET teachers with the skills and tools they need to digitise their lessons and make them more engaging for students. The project intends to bridge the gap between the recognized need for digitalization in VET and the lack of widespread adoption of digital tools and methodologies in classrooms across Europe.
Objectives of the Guidelines
These guidelines aim to:
- Improve the understanding among VET staff of available digital tools and approaches.
- Enhance teachers’ digital skills in terms of content creation.
- Illustrate the benefits of using Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) in VET.
- Provide an overview of the digital tools best suited for various VET disciplines.
- Offer practical examples of how to use digital tools to create innovative teaching content.
- Provide suggestions and advice for the design and implementation of effective digital lessons.
Context
Importance of Digitization in Education
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, education is undergoing a significant transformation. Digitalization offers numerous benefits, including:
- Enhanced Learning Experiences: Digital tools can create more interactive and engaging learning environments, catering to the needs of today’s tech-savvy generation.
- Personalized Learning: Digital platforms enable customized learning experiences that cater to individual student needs and learning styles.
- Access to a Wider Range of Resources: Digitalization provides access to a vast array of online resources, expanding learning opportunities beyond traditional textbooks.
- Development of Essential 21st-Century Skills: Digital tools help students develop critical skills such as digital literacy, problem-solving, and collaboration, which are essential for success in the modern workforce.
Link to the E-Learning
These guidelines are designed to complement the Di-struct! E-Learning course, which provides VET teachers with a comprehensive overview of digital tools and methodologies. The E-Learning course covers topics such as gamification, interactive presentations, online boards, interactive games, content creation, educational resources, Learning Management Systems, and online collaboration tools. To explore E-learning, the first step is filling this form to get the credential to access.
The guidelines will provide practical examples and specific instructions on how to apply the concepts learned in the E-Learning course to different VET disciplines.
Impact on Teaching Methods
Digitalization has a profound impact on teaching methods, encouraging a shift from traditional, teacher-centered approaches to more student-centered and interactive learning experiences. Digital tools enable teachers to:
- Create more dynamic and engaging lessons.
- Facilitate active learning and student participation.
- Provide personalized feedback and support.
- Promote collaboration and peer learning.
By embracing digital tools and adapting their teaching methods, teachers can create more effective and relevant learning experiences for their students.
Prepare Teachers for the Future of Education
The rapid advancements in technology are transforming the educational landscape. Digitalization is no longer a trend but a fundamental aspect of modern education. By acquiring the necessary digital skills and embracing innovative teaching methodologies, teachers can prepare themselves for the future of education and empower their students to thrive in a digital world.
Each section of the guidelines will be dedicated to a specific VET discipline. Each section will include the following elements:
- Introduction to the discipline and its specific digitalization needs.
- Recommended digital tools with descriptions, benefits, suggested target, if an installation on the laptop is required or not, usage examples, and the link to use it.
- Concrete examples of digitization in professional fields. Please note that the examples of digitization in professional fields contain documents or external links which may not be in your mother tongue. These documents are for information purposes, to show you how the teaching content is structured.
- Best practices for digitizing content, including needs analysis, tool selection, content adaptation, and implementation strategies.
- Methodology: Step-by-step instructions on how to structure and digitalize content effectively.
- Description and comparison of the SAMR and Gagné models, including examples and their relevance to digital content creation.
- Conclusion: Summary of key takeaways and recommendations for further exploration.
- Tips and comments from teachers, sharing real-life experiences and practical advice.
The Di-struct! project and these guidelines are committed to supporting VET teachers on their journey towards digitalization, empowering them to create engaging and innovative learning experiences for their students and contribute to the advancement of VET in Europe.
Benefits for teachers and students
- Increased accessibility of educational material that can be consulted synchronously or asynchronously by students, particularly in different learning situations (FEST = training outside the walls of the CFA, students with phobia or dropping out of school, students with special needs). This accessibility also makes it possible to make the courses accessible in the event of student absences.
- Inclusion of special needs: new technologies also make the transposition of our courses more simple for students with disabilities (voice reading, subtitles, possibility of switching content to dys mode).
- Pedagogical differentiation: digital educational content then makes it possible to adapt to the level of apprentices and avoid boredom for those with a high level and on the contrary discouragement for those with a lower level. AIs adapted to existing tools thus make it possible to quickly target the level reached in an exercise such as Quizlet and adapt to the participant. Some tools also offer feedback that can be easily used by the teacher, who will be able to adapt the next lesson according to the results obtained.
- Engaging and interactive content: the idea is not to multiply the tools in a senseless and thoughtless way, but some of them, extremely simple in their use, can bring dynamism and a necessary bounce back in the classroom. Especially in the case of a virtual classroom where the students’ attention is all the more of an issue.
- Efficiency and time saving: finally, familiarization with these tools allows you to gain in efficiency and therefore to save time in your pedagogical practice (to be reused elsewhere on a more personalized support for apprentices or other). Once you get the hang of it, the digital tool can therefore facilitate the teacher’s work by allowing them to reuse canvases that have already been established or by updating them.
Other benefits can be mentioned¹:

¹ How Technology is Changing Education? The Journey from Whiteboard to Keyboard https://www.apogaeis.com/blog/how-technology-is-changing-education-the-journey-from-whiteboard-to-keyboard/
Impact on teaching methods
Prepare teachers for the future of education (adaptation to digital environments, collaborative tools, etc.) and the evolution of society in general.
It is also a question of meeting the requirements of the labour market in which our apprentices are engaged. Mastery of software, use of collaborative tools, online tools – including in remote fields at the base of digital technology. Putting them in contact with digital technology as soon as possible also promotes their adaptability to future technological developments related to their professional field.
The school thus connects more to the professional world. Digital technology allows apprentices to get into the swing of their future professional practice and to project themselves.
The skills mobilized are also transversal and transferable to other fields. Learn to work remotely, learn to manage a schedule, encourage autonomy and critical thinking.
Opening up pedagogy to digital technology finally allows us to question the best practices to adopt, to promote an ethics of this use among our apprentices. This generally contributes to the formation of responsible citizens, aware of the ethical issues of digital technology.
Autonomy of future citizens after the school system. Teaching also means thinking about the + distant future of our apprentices and encouraging them to always improve their skills. Digital technology also plays a role in this evolution.
– New Gen-Z and Alpha methodology?
Gen Z (1997-2012) Gen Alpha (post 2013), globally the “digital natives”. Generations more used to short, dynamic and interactive content. They use social media on a daily basis, so the pedagogy going digital “speaks” to them more. Digital technology therefore represents an interesting learning lever to be mobilized for the commitment, interest and motivation of these apprentices who appreciate autonomy and interactivity.

To go further:
- EU support for the digitalisation of schools; 2023 (English version only)
- Digital Education Action Plan (2021-2027); (English version)
- How Technology is Changing Education? The Journey from Whiteboard to Keyboard
1. Note taking “Study smarter not harder”
- VET subject: Computer Science in a technical economic school, teaching coding to accounting students
- Overview: This learning unit focuses on enhancing students’ study autonomy through effective note-taking methods, time management strategies and the integration of digital tools. The addresses the challenges they face, such as difficulty organizing study time, low digital literacy, and inclusion of students with special needs.
The subject is highly transversal, as it supports all disciplines by equipping students with essential skills that improve comprehension, retention, and school performance. - Link to the learning unit: Note taking “Study smarter not harder”
2. Exploring fruit and vegetables in culinary technology
- VET subject: Culinary Technology
- Overview: This learning unit focuses on enhancing students’ understanding of Culinary Technology. Students will learn to identify and classify fruits and vegetables, understand quality and storage criteria, and comply with regulations. The unit combines theory and practice, emphasizing sustainable food practices and consumer demands. Interactive tools and gamification are used to motivate students, with assessments conducted through Microsoft FORMS and Escape Games on GENIALLY.
- Link to the learning unit: Exploring fruit and vegetables in culinary technology
3. Practice in 3D engineering design software systems
- VET subject: Practice in 3D engineering design software systems
- Overview: 3D Modeling, is a method used to create computer models of real-world objects for applications in machine engineering. At the heart of “Practice in 3D engineering design software systems” course is applied geometry where complex geometrical models are created by manipulating and combining basic shapes such as cubes, rectangular prisms, cylinders, spheres, and cones. In this course students learn CAD/CAM engineering software through hands-on practice. While building 2D and 3D models, they improve their geometry skills and develop strong spatial reasoning skills (ability to “think in the 3D space”). Upon completing the course, students are ready for a smooth transition to using professional CAD software such as Solide Egde engineering design software.
- Link to the learning unit: Practice in 3D engineering design software systems
4. Business and databases
- VET subject: Business and databases
- Overview: The main goal of this unit is to provide students from both courses with management and database structuring skills/expertise. Students from the Business Course should explain the requirements for creating a customer database that meets the needs of the commercial department and students from the IT Systems Management and Programming course should exchange concepts about database structure requirements. The joint activities help students to see how different areas of management are interconnected in the context of a real company. Activities include research, Teamwork using Canva to create presentations, Whiteboard to create interaction between the two classes with assessments conducted through Moodle Quiz and Kahoot.
- Link to the learning unit: Business and databases
5. Food4all
- VET subject: Cooking Technology, Restaurant Management and Bar-Tendering
- Overview: This unit focuses on enhancing students’ understanding of Italian regional foods and drinks, with an emphasis on their labeled products. It aims to build culinary vocabulary in English and Italian and develop skills in planning and presenting projects. Activities include research, digital content creation, and a Kahoot battle to assess knowledge. Students work on individual and team tasks using tools like Canva, Padlet, and Google Slides to create engaging presentations. The approach encourages collaboration, digital proficiency, and self-assessment, fostering confidence and creativity.
- Link to the learning unit: Food4All
6. Fascism and Futurism Decades
- VET subject: Food Service and Bar Tendering, Food Science
- Overview: It explores the rise of Fascism in Italy and its social, political, and cultural impacts, particularly focusing on propaganda’s role in shaping Italian gastronomy and beverage culture. Students analyze the influence of intellectuals, such as Futurists, on Fascist ideals and study how food and drinks became tools for national identity. Activities include case studies, creative tasks like designing propaganda-inspired cocktails, and debates to enhance understanding. The unit employs digital tools like Youtube videos to provide inspiration and PowerPoint or Canva to foster collaboration and critical thinking.
- Link to the learning unit: Fascism and Futurism Decades
7. Foundations of machine engineering
- VET subject: Machine Manufacture design
- Overview: A complex two-grade subject including engineering drawing, mechanical materials, safety at work, and basic metalworking. It helps to develop the students’ mechanical engineering mindset. Learners will be able to carry out tasks with responsibility and make decisions in project work. The course is an important part of the sectoral basic examination.
- Link to the learning unit: Foundations of machine engineering
8. Circular Economy, Start-Ups and Anti-waste Catering
- VET subject: Food and Wine Service, Food Science, Economics
- Overview: This unit addresses sustainability through topics like Agenda 2030, Circular Economy, Green Economy, and Food Waste, emphasizing the future of sustainable catering. It combines gamification, cooperative learning, and digital tools to explore critical consumption, startups, and green practices in various industries. Activities include quizzes, videos, case studies, and creative tasks like recycled crafts and escape room creation. Tools like Canva, Mentimeter, and Google Docs foster collaboration and engagement while enhancing language skills via CLIL methodology. The focus is on empowering students to connect global challenges with practical solutions.
- Link to the learning unit: Circular Economy, Start-Ups and Anti-waste Catering
9. Converting Masses in Culinary Arts
- VET subject: Culinary Technology
- Overview: This unit focuses on improving apprentices’ ability to convert measurements in the kitchen, addressing the challenge of applying theoretical math skills to practical tasks. It enhances their speed, autonomy, and accuracy in using kitchen tools and following recipes.
The subject is transversal, supporting various culinary disciplines by equipping apprentices with essential skills to work efficiently and accurately, with the help of digital tools like WOOCLAP, SWAY, and QUIZLET. - Link to the learning unit: Converting Masses in Culinary Arts
Prerequisites
Am I comfortable with digital tools?
✓ Yes: list and bookmark the available tools. When there are many of them, remember to classify them according to their uses (quizzes, presentations, exercises, memorization, getting people to collaborate, practising speaking, working on writing, etc.).
✗ No: apply the First Small Step Possible method, i.e., choose a small educational action (welcome, end of class, an exercise, etc.) to dare to get started. Target a tool that is available and if possible mastered by a colleague to get help easily. Another solution is to watch a tutorial to get to grips with the tool more quickly.
Methodology: Basic steps to structure and digitize content (needs analysis, selection of tools, design of digital resources).
1. Needs analysis
- What are the skills to be developed provided for in the framework (according to Bloom’s taxonomy: knowledge, understanding, application, analysis, synthesis, creativity/evaluation)?
- What are the specific learning objectives (content, behavior, conditions)? E.g. “At the end of the activity/lesson, the student will be able to use the targeted vocabulary in the various contexts of his or her profession.”
- What kind of knowledge do learners acquire? Declarative knowledge (vocabulary, comprehension, concept) or procedural knowledge (automatisms, know-how, method)?
- When would a digital tool be relevant? For example: beginning of the session (reactivation, prerequisites, surprise effect or complex question, …), during the session (to summarize, check understanding, practicing, …), at the end of the session (summarize, question, announce the rest, …), during an evaluation or a complex task, for work to be done at home. Or for example :
- Why would a digital tool be relevant?
To take into account the 4 pillars of learning:
✓ Attention: capturing and keeping attention can be facilitated by digital tools. Ex : use Classroom-screen to create a stimulating virtual environment.
✓ Active engagement: Every learner should be able to participate. Ex : incorporate Wooclap for interactive real-time polls and quizzes.
✓ Feedback: Instant feedback is very effective. E.g . use Quizlet for self-correcting exercises or Wooclap for collective remediation.
✓ Consolidation: forgetting happens very quickly! Short, regular and spaced practice helps to counter forgetfulness and memorize! E.g . offer Learning-Apps or Quizlet for review activities.
To make training courses accessible to all (e.g . disability, neuro-atypical, absent) and/or to offer a variety of assessment materials or learners’ choice (universal design of learning).
To promote multimodality in the presentation of knowledge, proposed learning tasks and assessments. E.g . face-to-face/remote, synchronous/asynchronous, auditory, visual (static/dynamic), …
To make experiences possible that are impossible without digital technology. E.g . collaborating on the same document at the same time; collaborating remotely; carrying out scientific experiments without risk, without equipment, without consumables; talking to a virtual teacher who asks questions; being corrected in real time, etc.
→ teacher’s choice of a tool, activity, theme and learning objective
→ choice by the learner of a deliverable medium (audio, video, written, mind map, quiz, …)
Content creation
- What media do I already have? E.g . books, digital books, course materials, exercise sheets, teachers’ websites, etc.
- Can I adapt/integrate these media?
✓ Yes: use screenshots, existing files to import them into digital tools directly or via the tool’s AI.
✗ No: check whether similar content is available online, in the databases.
✓ Yes: use them as is or adapt them
✗ No: Create your own content
- How can I personalize the content? With elements of the profession, the course, the institution, the group (e.g. choice of examples, photos, videos, …)!
- How to classify the various digital resources? You can classify the digital resources in the tools themselves, in folders, in your browser’s favorites, etc.
Implementation
- Create a session or a sequence integrating one or more tools directly into your workspace (Moodle, Yparéo, Pronote, etc.) or on other media.
- Integrate the different media and digital tools in a coherent way in the course. E.g . copy/paste internet links or QR codes to integrate these digital activities, find them easily or offer them to learners synchronously or asynchronously.
- Plan to deal with technical issues (e.g . wifi, internet connection) and time to appropriate the tools with the learners.
Evaluation and continuous improvement
- How did the learners perceive the proposal? Have they understood the pedagogical intentions and the interest of the proposed task (metacognition)? How can the practice be improved? To question them to gather their opinions and make them actors in their training. (e.g . orally, in writing, using digital tools such as Forms).
- What were the obstacles to learning and how can they be overcome? E.g . technique, cognitive overload, instructions, time, too “easy” or too “hard”, lack of explanations…
- How to track learners’ progress? Formative assessments are powerful training tools because they allow learners and teachers to measure progress and address challenges. Digital assessments allow all learners to assess themselves, train their long-term memory, counter forgetfulness and identify difficulties. They allow the teacher to monitor progress and to take over the points not acquired. E.g . Wooclap, Quiziniere, Learning-Apps, Quizlet, Quizziz, GoogleForm, are all tools for this.
- Do I need training to progress in the use of digital technology?
✗ No: the practice and use of digital tools naturally allows me to progress and gain in speed and automatisms
✓ Yes: I reach my limits. I’m looking for training or other tools! E.g . with colleagues, watching tutorials or participating in webinars, browsing galleries of examples, requesting Adhoc training, following MOOCs, subscribing to educational newsletters, following inspiring sites or accounts, etc.
Short description: Microsoft Whiteboard provides an intelligent, free-form canvas for imagining, creating and collaborating visually. It lets you write or draw, enter text, add an image, sticky notes or a note grid to express your ideas, and use feedback to visually communicate your thoughts.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students
Example of application: Business and databases
Installation required: yes (app)
Link: www.microsoft.com/en/microsoft-365/microsoft-whiteboard/digital-whiteboard-app
Short description: Kahoot! is a playful learning platform. It includes learning games such as multiple-choice quizzes. It is accessible via a web browser, but can also be downloaded to a smartphone. This educational platform is similar to other technological learning tools such as Wooclap, Wooflash, Socrative and Quizlet.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students
Example of application: Business and databases , Practice in 3D engineering design software systems
Installation required: no
Link: https://kahoot.com/
Short description: A web-based presentation tool allowing users to create, edit, and share presentations.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students, individual students, teachers
Example of application: Foundations of machine engineering
Installation required: no
Link: https://workspace.google.com/intl/en_uk/products/slides/
Short description: Miro is a digital collaboration platform designed to facilitate remote and distributed team communication and project management.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students, individual students, teachers
Example of application: Note taking “Study smarter not harder”
Installation required: no
Link: www.miro.com
Short description: Evernote is a versatile note-taking tool designed to help you organize your ideas, tasks, and projects. It allows you to create notes, save web content, manage to-do lists and collaborate seamlessly across devices, ensuring information is always available.
Suggested target: individual students
Example of application: Note taking “Study smarter not harder”
Installation required: no
Link: http://www.evernote.com
Short description: Microsoft OneNote is a digital notebook that allows users to capture, organize, and share notes across devices. With features like text, drawings, images, and multimedia support, it’s perfect for managing tasks, collaborating on projects, and keeping ideas in one place.
Suggested target: groups of students, individual students, teachers
Example of application: Note taking “Study smarter not harder”
Installation required: no
Link: https://www.onenote.com/
Short description: A graphic design platform that offers various templates and tools for creating infographics, posters, presentations, and more.
Suggested target: groups of students, individual students, teachers
Example of application: Food4All
Installation required: no
Link: http://www.canva.com
Short description: Microsoft PowerPoint is a presentation software. It is part of the Microsoft Office suite. It can be used to create both simple slide presentations and complex slide shows.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students, individual students, teachers
Example of application: Fascism and Futurism Decades
Installation required: no, available offline as well
Short description:
Lib Manuels is a digital platform offering a digital and interactive version of textbooks and educational resources for students and teachers. It provides easy access to a wide range of digital learning materials, enhancing teaching and learning experiences through interactive tools and seamless navigation.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students, individual students
Example of application: Exploring fruit and vegetables in culinary technology
Installation required: no
Short description: A digital tool that allows us to create interactive exercises, presentations, images, quizzes, portfolios and much more. In this tool you can enrich your classes with animation and interactivity within seconds.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students, individual students
Example of application: Exploring fruit and vegetables in culinary technology
Installation required: no
Link: https://genially.com/
Short description: Google Forms is a survey administration software included as part of the web-based Google Docs Editors suite. Google Forms is only available as a web application. It allows users to create and edit surveys online and to collect information into a spreadsheet.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students, individual students, teachers
Example of application: Exploring fruit and vegetables in culinary technology
Installation required: no
Short description: OER Commons provides a curated collection of free and open educational resources for teaching and learning. This platform offers a variety of high-quality materials, including lesson plans, activities, and interactive content, empowering educators to share, discover, and customize resources for their classrooms.
Suggested target: teachers
Example of application: Practice in 3D engineering design software systems , Foundations of machine engineering
Installation required: no
Link: https://oercommons.org/
Short description: Edpuzzle is an interactive learning platform that allows teachers to create engaging video lessons. Educators can customize videos by adding questions, notes, and voiceovers to track student progress and understanding, making learning more personalized and effective.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students
Example of application: Practice in 3D engineering design software systems
Installation required: no
Link: https://edpuzzle.com/
Short description: Video platform to show videos to your classroom.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students, individual students
Example of application: Practice in 3D engineering design software systems
Installation required: no
Link: https://www.youtube.com/
Short description: Baamboozle provides an easy and enjoyable way to teach through games that are both engaging and tailored for students. With a wide variety of games and a user-friendly editing tool, the platform allows the community to create and customize content.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students
Example of application: Foundations of machine engineering
Installation required: no
Short description: A learning management system that enables teachers to create, distribute, and manage assignments, resources, and assessments.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students
Example of application: Circular Economy, Start-Ups and Anti-waste Catering
Installation required: no
Link: https://edu.google.com/intl/ALL_uk/workspace-for-education/classroom/
Short description: Mentimeter is an online platform for creating polls, surveys, interactive questionnaires and real-time presentations. It is used to interact with the public and gather responses. Here are some of the main features offered by the tool: Dynamic word clouds; Live interactive polls; Quizzes; Surveys
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students
Example of application: Circular Economy, Start-Ups and Anti-waste Catering
Installation required: no
Short description: Quizlet allows teachers to create digital flashcards and quizzes. It can also be used to create multiple-choice, true/false and fill-in-the-blank tests.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students
Example of application: Converting Masses in Culinary Arts
Installation required: no
Link: https://quizlet.com
Short description: A survey and quiz creation tool that enables teachers to create assessments and gather feedback.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students
Example of application: Converting Masses in Culinary Arts
Installation required: no
Link: https://www.wooclap.com/
Short description: Sway is a Microsoft Office application that allows you to easily create and share interactive reports, personal stories, and presentations without needing design skills.
Suggested target: entire class, groups of students
Example of application: Converting Masses in Culinary Arts
Installation required: no
IF YOU WOULD LIKE TO DISCOVER MORE DIGITAL TOOLS, YOU CAN HAVE A LOOK AT THESE SLIDES
The chapter of ” Why digitalize educational content?” focused on the students’ benefits of digitally enhanced lessons, in other words you can understand the WHY. In this chapter, we introduce you to the HOW and present two models for digitizing lessons that you can use easily and effectively in your everyday teaching practice. Both are closely linked to the findings and outcomes of the project. These two models are SAMR and Gagné’s Nine Events of Instruction. But whichever one you use, your pedagogical goal always must be to find the right tools for your learners. To develop the right learner focused technology integration, you have to think about a few key questions:
- How can Your lesson be improved using technology?
- How can You engage and empower students through technology?
- How can digitally enhanced learning closely resemble authentic, real-world learning?
SAMR – the model for understanding the right integration of technology and EdTech
The model, which has been in use since the mid-1990s, is based on the fact that there are different stages of integration of digital tools and technologies in education. It is a hierarchical model, which assumes that there is a clear qualitative difference between each level and that moving from one level to another needs teaching/learning pedagogical innovation for the institution, teacher, and student group (class).

Furthermore, the model states that the educational integration of technology at each level depends on the level of teachers’ and learners’ digital pedagogical and learning competences and knowledge of using EdTech tools, the scale of their application (what they are used for: digital content, online learning, knowledge assessment, communication between the stakeholders, active cooperative learning, etc.) and, last but not least, the development level of the institutional (school) policy, practices and culture (innovative open educational supportive climate) that support the EdTech integration into the teaching and learning process.
Let’s see the four hierarchical levels of technology integration:
S – Substitution. Technology just replaces a traditional teaching activity and/or material in the educational practice without a significant methodological change. This could be the use of digital presentation tools instead of writing on a blackboard, the use of pdf, e-book instead of the traditional textbook, or even an online test and posting online using Microsoft OneDrive, Google Drive, or a similar file-sharing service. If you have only been teaching with classical tools, this could be a good start to integrate EdTech tools into your teaching practice.
A – Augmentation. In comparison to simple substitution, the use of technology in education at this level means extending the learning process with digital tools that support learner interactivity and involvement. The use of technology gives an opportunity for interactivity, learner feedback, and active involvement of the learner in the learning process, but the use of traditional methodology is typical. An example could be, when students receive immediate feedback on their performance from the teacher or peers, for example using Kahoot, LearningApp, or Quizizz. However using a Padlet also allows for active learner engagement.
In the first two levels, the integration of EdTech can improve student engagement by making learning more fun and playful, but in the longer term, if we don’t change the tools we use, this motivation improvement may disappear.
M – Modification. At this level, EdTech tools allow us to change the teaching and learning process, to change the roles of the teachers and learners, thus improving skills to make the learning flexible and meet the learning needs of the students. It allows the development of 21st century competencies too. These could be the implementation of online or blended/hybrid project activities, where learners can work independently, in groups online, research, find information, and think together to create a subject-specific product while developing important skills.
R – Redefinition. At this level a complete rethinking of teachers’ work and activities, change in the content and learning processes, with the integration of technology for learning are taking place. This enables learners to learn through solving creative problems that were not possible before. Using VR and AR, virtual work placements (even international ones) can be implemented. Technology also provides opportunities to bring authentic audiences into the virtual classroom. Students can tackle local problems and invite members of the community to assess their digital proposals.
Gagné’s model for increasing learning engagement of the students
The following model is an excellent way of enriching a teaching module, a lesson, or a learning unit, by using an EdTech tool and thus improving the learning motivation and experience of the learners. The basis of this extremely usable model in practice is to identify the points of the learning process where the learner’s learning motivation can be influenced using traditional and/or digital tools. Although originally Gagné did not develop the model for enriching learning/teaching with the use of digital tools, the model is perfectly suited for this purpose. What is important for 21st century education is what EdTech tools can be found to influence learner effectiveness at these points of stimulation identified by Gagné. The tools need to fit the learning behaviours and needs of learners in the 21st century, so they need to be EdTech tools as well.

Using the model, you, as a teacher must identify to stimulate the learners’ motivation on the following points during the learning process:
- Gain attention – Get the students primed and focused, so they are ready to learn the topic at hand. Use animations, videos, interactive stuff & games, VR/AR tools, and give them tasks
- Inform learners of objectives. –Tell students what they will learn during the lesson to get them in the proper state of mind so they can anticipate what they will need to do afterward. Use visual communication tools, like Canva; LMS Tools, like Moodle, Google Classroom, Blackboard; Goal-Setting Apps, like Trello,
- Stimulate recall of prior learning – Prime students for learning new material by refreshing their memories of prior-learned content. Use Kahoot, Quizlet, Quizzes, Baamboozle, flashcards, or any other quiz tool (stand-alone or integrated with any LMS system)
- Present the content – Once the environment is ready and students are receptive and primed, it is time to teach the applicable lesson. Use video platforms, Edpuzzle (interactive video), TED-Ed; Interactive presentations, like Genially, SlideShare, Haiku Deck, Interactive/digital eBooks, and customizable LMS, like Moodle
- Provide “learning guidance” – Explain clearly to students what is expected for them to understand and any instructions needed to achieve successful outcomes. Use guided practice tools, like Khan Academy, PhET Interactive Simulations; Real-Time Feedback: Classkick, Formative; Digital Note-Taking: Evernote, Notion, OneNote, and AI Tutors
- Elicit performance (practice) – Instruct students to practice or demonstrate their newfound knowledge so it can be assessed. Use Interactive exercises, simulations, digital labs, and games to practice. H5P (interactive content creation), Kahoot, Mentimeter, online project collaboration tools, like Google Workspace (Docs, Sheets, Slides), Microsoft Teams, and/or customised LMS, like Moodle.
- Provide feedback – Offer immediate feedback on student tasks that is personalized, constructive, and positive. Use online/blended/hybrid tools for peer/group/teacher feedback;
- Assess performance- Conduct a comprehensive assessment to determine how well students met their learning objectives so learning gaps can be addressed. Use Kahoot, Quizlet, Quizzes, Baamboozle, flashcards, or any other quiz tool (stand-alone or integrated with any LMS system). Adaptive Testing Tools, H5P, and Game-Based Assessments, like Minecraft Education Edition, ClassDojo, Digital Portfolios: Seesaw, and Google Sites.
- Enhance retention and transfer – Teachers should do everything possible to help students retain the information they worked so hard to learn and give them chances to personalize their learned experience to apply it to their own life or job. Use Scenario-Based VR Tools, simulations (OpenSimulator), E-Portfolios, Real-Life Applications like Google Earth (geography projects), Wolfram Alpha (real-world math/science).
Further readings
The Di-Struct project has demonstrated that digitalization in Vocational Education and Training (VET) is not just an option but a necessity for modern teaching. By integrating digital tools, interactive methodologies, and adaptive learning strategies, educators can significantly enhance student engagement, accessibility, and skill acquisition.
Moreover, digital tools play a crucial role in lifelong learning, enabling both teachers and students to continuously update their knowledge and competencies in an ever-evolving technological and professional landscape.
In this context, digital resources not only facilitate the learning process but also help educators stay aligned with industry advancements, ensuring that vocational training remains relevant and effective.
However, this transformation requires a structured approach, ongoing experimentation, and strong institutional support to maximize the benefits of digital education.
Key Insights from the teachers after the Testing Phase
- Digitalization increases engagement, but balance is key
- Tools like LearningApps, Kahoot, Wooclap, and Microsoft Whiteboard enhanced student participation, making lessons more interactive.
- However, excessive or unstructured use of digital tools can overwhelm students and teachers, making it crucial to carefully align technology with learning objectives.
- Personalization and accessibility improve learning outcomes
- Digital resources help accommodate different learning paces, special needs, and remote learning situations.
- AI-based tools such as Quizlet and adaptive learning platforms can tailor lessons to individual proficiency levels.
- Blended learning and interdisciplinary approaches work best
- The most successful lesson plans combined digital activities with traditional, hands-on experiences—particularly effective in fields like Culinary Technology, 3D Engineering, and Business and Databases.
- Interdisciplinary collaboration, such as integrating business management with IT applications, helped students make real-world connections between different fields.
- Flipped classrooms require gradual implementation
- Providing students with digital resources before class (e.g., OER videos) was beneficial, but many saw it as extra homework.
- Schools should cultivate a flipped learning culture by guiding students on how to engage with pre-class content.
- Teacher training and collaboration are essential
- Many teachers faced digital literacy challenges and resistance to new tools. However, peer learning and structured training programs improved confidence and innovation in lesson planning.
- Collaborative tools like Miro, Microsoft Teams, and Padlet facilitated teamwork among educators, leading to co-creation of high-quality digital content.
- Challenges remain in infrastructure and digital dependency
- Over-reliance on cloud-based tools poses risks, such as data loss due to platform changes.
- Unequal internet access and device availability created digital divides, requiring backup strategies for offline learning.
Frameworks for Digital Integration
Integrating digital tools into vocational education requires not only technical proficiency but also a well-structured pedagogical approach. The implementation of digital resources must be guided by clear educational objectives, ensuring that technology enhances, rather than replaces, effective teaching strategies.
The adoption of pedagogical models, such as the SAMR Model and Gagné’s Nine Events of Instruction, provides a structured framework that helps educators integrate technology at different levels, from basic substitution to complete redefinition of learning experiences. These models encourage a strategic and thoughtful use of digital tools, ensuring that learning remains engaging, interactive, and aligned with students’ needs. By following such structured methodologies, teachers can create digital lessons that foster student autonomy, critical thinking, and practical application of knowledge, ultimately improving learning outcomes in VET education.
Looking Ahead: A Sustainable Digital Strategy
For VET institutions to fully leverage digital transformation, future efforts should focus on:
Continuous Professional Development: Regular training for teachers on emerging EdTech tools and digital pedagogy.
Structured Digital Learning Strategies: Establishing clear digital policies to balance online and offline learning.
Scalability & Infrastructure Investments: Ensuring internet accessibility, device availability, and long-term digital sustainability.
AI & Emerging Technologies: Exploring Artificial Intelligence for adaptive learning, Virtual Reality (VR) for immersive training, and gamification for motivation.
While digital tools offer numerous advantages, their integration requires teachers to overcome challenges such as adapting to new technologies, managing digital distractions, and rethinking traditional pedagogical strategies. Future training programs should focus not only on digital skills but also on change management and pedagogical adaptation.
The integration of generative AI tools enables teachers to harness this technology to design innovative teaching activities that leverage digital resources while adhering to established pedagogical methodologies. Generative AI proves valuable in both the brainstorming phase—helping educators explore creative approaches and refine learning objectives—and the production of high-quality teaching materials.
As we integrate AI and digital tools into education, it is crucial to ensure ethical use, data privacy protection, and a balance between digital and human interaction to maintain student well-being.
By streamlining content creation and ensuring alignment with effective teaching strategies, AI empowers educators to develop engaging, structured, and pedagogically sound learning experiences that enhance student participation and comprehension.
Final Thoughts
Digital transformation in VET is an evolving process that requires experimentation, adaptability, and collaboration. The Di-Struct project has laid a strong foundation for integrating technology in vocational education, but the key to long-term success lies in continuous learning, iterative refinement, and institutional commitment.
The recommendations and guidelines produced by the Di-Struct project must be continuously adapted and expanded to keep pace with the rapid evolution of digital technologies in education. As new tools, methodologies, and AI-powered innovations emerge, it is essential for educators and institutions to remain flexible, reassess their strategies, and ensure that digital transformation aligns with both pedagogical best practices and the evolving needs of students and industries.
By embracing digital tools strategically and responsibly, educators can empower students with 21st-century skills, preparing them for a workforce that increasingly demands digital proficiency, adaptability, and interdisciplinary problem-solving abilities.
If you would like to explore the E-learning “VET going digital” it is possible by filling this short form: https://www.di-struct.eu/elearning/
An email with the instructions and the credentials will be sent to access e-learning a few days later.
If you would like to use the template of the learning material shared to VET teachers to get your lessons more digital, you can:
- Download this learning unit template and develop your new lesson plan
- Use this Miro board: after testing your new lesson plan with your students, create a similar board to think about what worked, what didn’t, how effective they were, how students responded and what could be improved.
Please explore the Miro board and the VET schools involved as an example.























